
Protein transport between cells
We study how glycan-protein interactions affect protein diffusion, distribution and function in extracellular matrix
Background
Extracellular signalling proteins are essential for cell-cell communication: morphogens guide tissue development, chemokines guide the migration of immune cells to sites of infection, and growth factors guide tissue repair. Proper function of these proteins relies on their proper distribution (e.g., as gradients) and movement in the extracellular space.
Many extracellular signalling proteins bind extracellular matrix polysaccharides of the glycosaminoglycan (GAG) family. Toxic proteins and viruses also exploit extracellular glycans to navigate the extracellular space and reach their target cells.
The Richter Lab aims to understand how such interactions regulate protein distribution and transport. To this end, we are probing how proteins diffuse and distribute in native and well-defined model extracellular matrices that are rich in GAGs and other glycans.
This research can enhance scientific understanding of how macromolecules diffuse in extracellular space to perform their functions, and how this process can be modulated in disease and therapy.
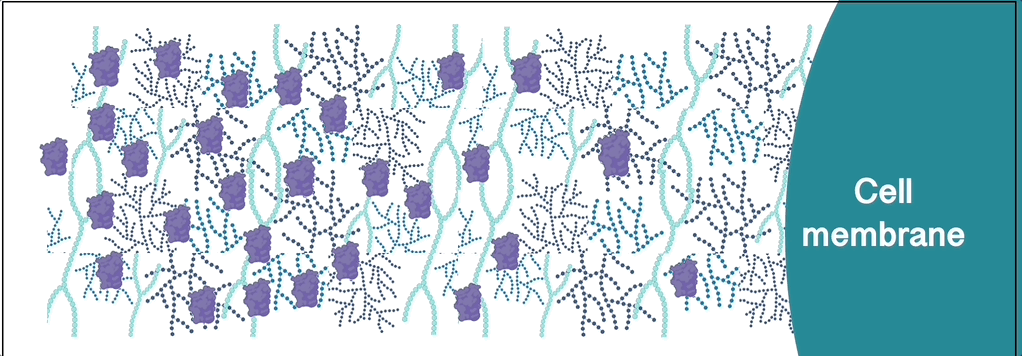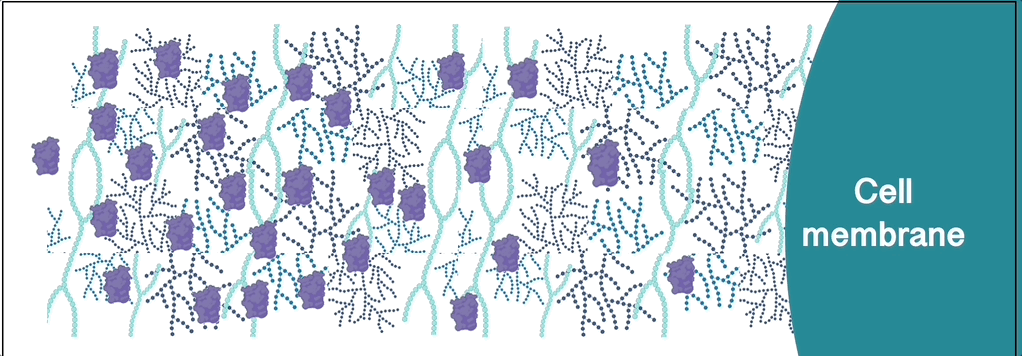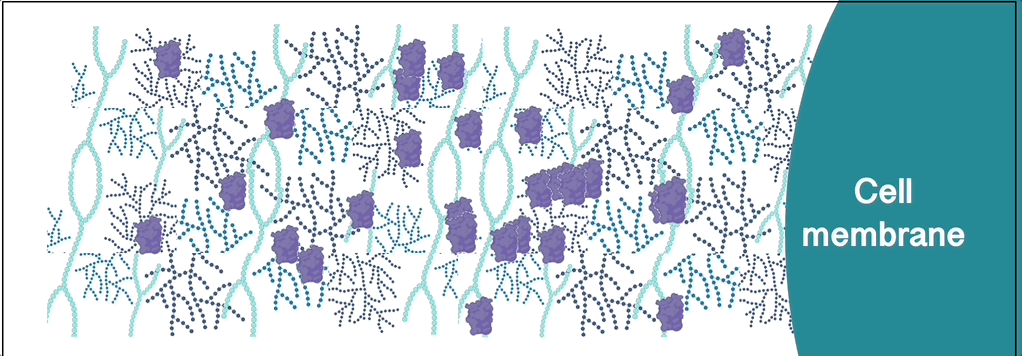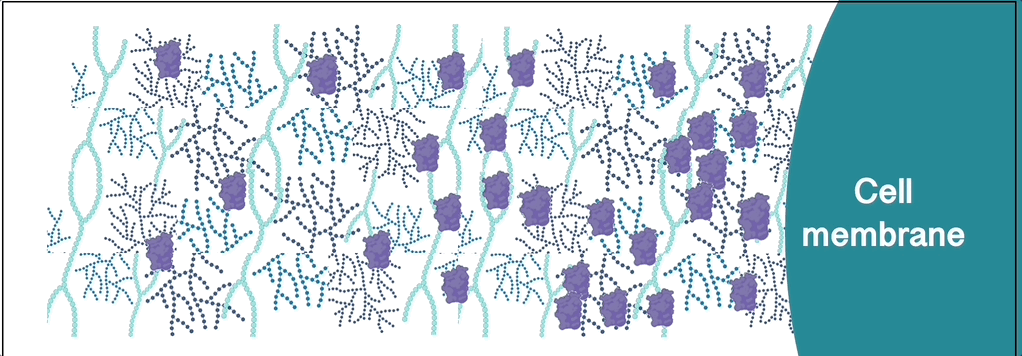

Tools used within our protein transport research
Click on each icon to learn more about the technique, and how it is used in our research
Read more here...
Chemokine CXCL4 interactions with extracellular matrix proteoglycans mediate widespread immune cell recruitment independent of chemokine receptors
A. L. Gray, R. Karlsson, A. R. E, Roberts, A. J. L. Ridley , N. Pun , B. Khan , C Lawless ,R. Luís , M. Szpakowska, A. Chevigné , C. E. Hughes, L. Medina-Ruiz , H. L. Birchenough, I. Z. Mulholland, C. L. Salanga, E. A. Yates, J. E. Turnbull, T. M. Handel, G. J. Graham, T. A. Jowitt, I. Schiessl, R. P. Richter , R. L. Miller and D. P. Dyer . Cell Rep. 2023, 31:111930




